1) Open Trading Account with a Regulated Forex Broker
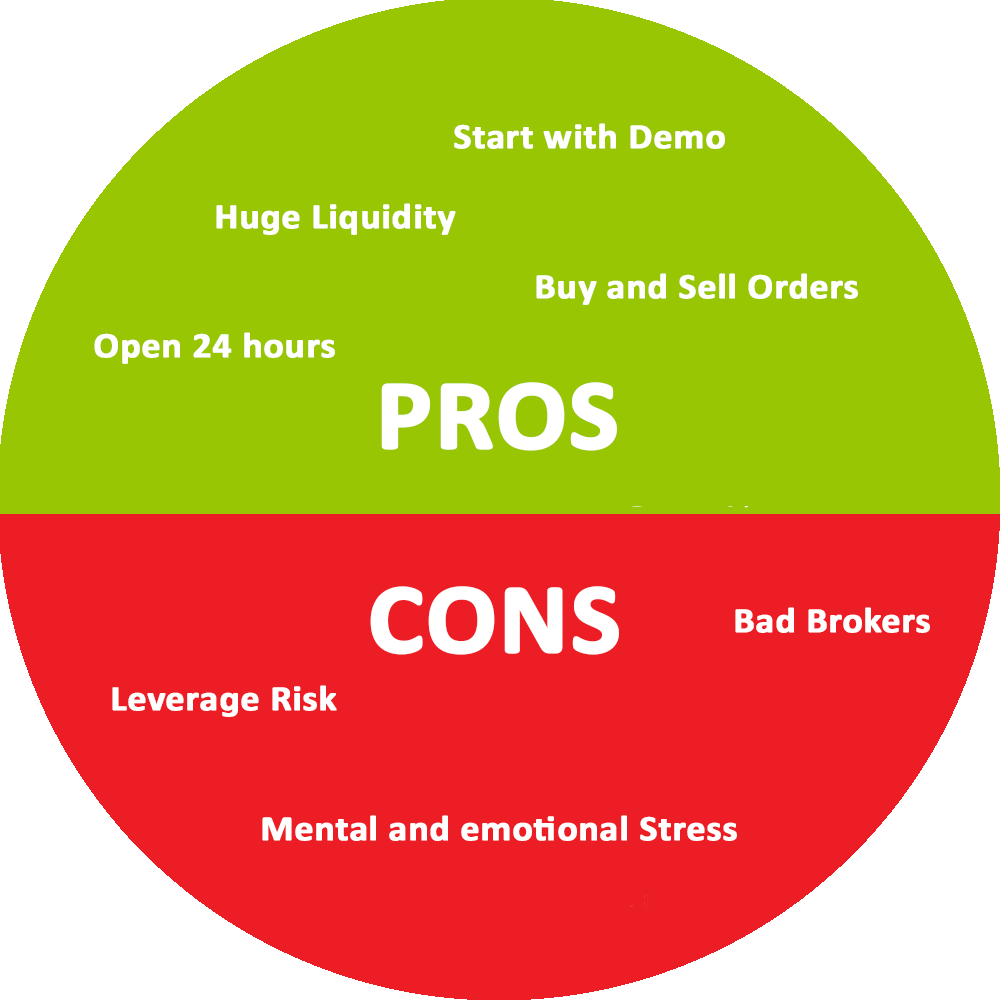
The first step to start trading forex is to choose a reputed & regulated forex broker, and then open an account with it. Choosing a 'good' broker is an important step because the broker plays a pivotal role in your trade.
There are many regulated forex brokers that accept South African traders: Hotforex (FSCA Regulated), XM Trading, Exness, Forextime, Avatrade, FxPro, and so many others.
You should also decide on the Account Base Currency that you want to choose. Some SA forex brokers offer ZAR Base Currency Account & this is useful in some cases. Also, your forex broker should accept deposits & withdrawals in ZAR via Bank Transfers & EFT.
We have compared & listed the best forex brokers for South African traders. We have only selected the brokers that are regulated (with atleast 2 regulators including FSCA, FCA, ASIC, CySEC), have competitive trading fees, and transparent record for fair dealing practice in the past.
Hotforex is our #1 recommended broker for Forex trading in South Africa.

- 1.2 pips spread on average for EUR/USD with Premium Account (no deposits & withdrawals fees). 0.3 pips on average for EUR/USD with Zero account.
- A Free demo Trading account is available at Hotforex
- Fast Order Execution & 100% STP broker
- 53 Currency Pairs, CFDs on Commodities, Indices, Metals & 1000s of global Stocks
- MT4 & MT5 platforms for mobile, web & desktop
- Deposits & Withdrawals are available via Internet Banking transfers.
- ZAR Accounts are available.
- Quick Withdrawals & excellent 24/5 chat support without any hold time.
- Funds safety – Hotforex is regulated with South Africa's FSCA (FSP No. 46632), UK's FCA (Financial Conduct Authority) & CySEC (Cyprus's Securities and Exchange Commission).
Start Trading at Hotforex Important: Forex Trading involves high risk, and your capital is at stake. Almost 75% of the traders lose money, so have a solid trading strategy that you have tested on demo account before trading with real money.
Note: Before you open your trading account with any forex broker, make sure to check that it is licensed or authorized by the FSCA for offering derivative instruments. FSCA have a public search on their website where you can find all the licensed & authorized brokers. Some brokers may claim to be authorized but may actually be unlicensed.
Also, it is important to note that some fake forex brokers may use the license number of an authorized broker on their website, claiming that they are authorized, which may not be a true claim. So, always make sure to ask the broker for their 'FSP Number' & then verify the number on FSCA's public search. Check the products for which the broker is licensed. And verify that you are opening account on the website actually licensed by the Regulator, avoiding any clones.
For example, Tickmill South Africa is authorized by FSCA under FSP No. 49464. They are approved under CATEGORY I for offering Derivative instruments, Shares & Forex Investment as an Intermediary.
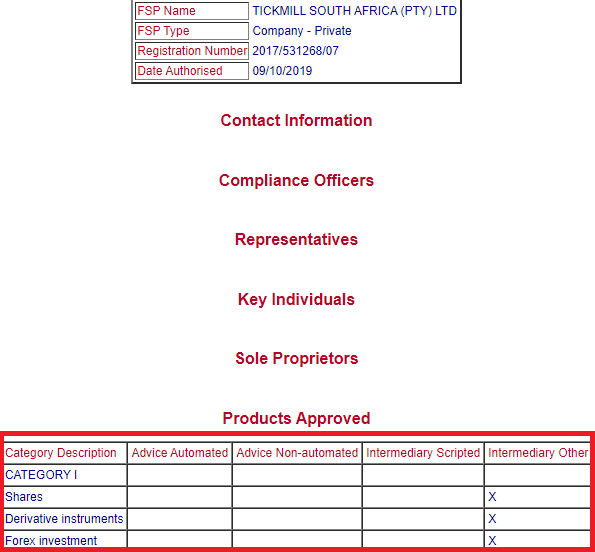
Trading with a licensed & reputed broker will ensure the safety of your funds, comliance by the broker, and redressal of issues in case of any dispute.
After you have made your choice on the broker, you then need to open your trading account with that broker. Almost all regulated brokers offer a demo account, we recommend you to practice first on a demo account & build your trading strategy before moving to live.
Note: All the regulated forex brokers require that you submit your ID proof & Address proof for verification (KYC). For ID proof, you can normally submit your Driver's License, and a Home Utility Bill of your Residence for the Address proof. You must verify your account before you can start trading live on any broker's platform. Opening a demo account does not require KYC, but it will be required when you are opening a Live Account.
An important question is how much money is required to start forex trading in South Africa? The minimum deposit required for account opening at some of the regulated forex brokers is as low as $1. In ZAR the minimum is R70 at Hotforex. But it is advised to start with a capital that is not too low, otherwise you are likely to use very high leverage in order to gain more profits. And this puts your entire trading capital are huge risk with every trade.
2) Understanding Forex trade
We will first dive into some important terms that you would need to know while placing your trade.
1. Lot Sizes: In Forex, you either buy or sell a currency pair in ‘Lots’. The Lots are simply united of currency that you are trading & have different names based on the number of units.
There are mainly lot sizes i.e. the Standard lot, Mini lot & Micro Lot. 1 'Standard Lot' means 100,000 units of Base Currency. 1 'Mini Lot' means 10,000 units of Base currency while 1 'Micro Lot' involves 1000 units of Base currency. The number of lots that you can trade will depend on factors like leverage, margin, your risk threshold etc.
The Profit & Loss will depend on the lot size. For example, you are trading EUR/USD, then with 1 Mini Lot, the movement of 1 pip is 1 USD.
Similarly, if you are placing trade for 2 Standard Lots (200,000 units), on GBP/USD, then the pip value will be $20/pip.
It is important to note that sizing up your trading position & only placing order for the right number of lots according to your risk is really important. Otherwise you risk losing your total capital in a single trade. Let's understand this with an example.
Let's say you have $1000 account balance, and you are placing order of 1 Standard lot on EUR/USD using leverage (explained below), then you are are risking too much on your forex trade.
If the trade goes against you by just 100 pips, which is less than 1% in case EUR/USD is currently at 1.1100. You risk losing your entire account balance on a single trade.
So, your position sizing (total lots) should be calculated according to your risk.
2. Leverage: Leverage, by definition, essentially involves borrowing a certain amount of money to invest in something. In Forex, if you are using leverage then it means, you are borrowing some money from your broker to place order for a bigger position than your actual capital. Sounds confusing? Don't worry, and follow through the following example.
Let's say that you want to place buy order for 1 standard lot (100,000 units) on EUR/USD. To trade this positive you would need $100,000 capital in your account. But what if you can lend money from your broker, and place the order. Let's say you use 1:20 leverage, then you would now need 1/20th of the capital to place that trade, and can now place the order with $5000 capital.
But Leverage is kind of a double-edged sword which has the potential to increase your profits if you are right, but also increases the risk of a bigger loss to you if you are wrong. A leverage of 100:1 allows the trader to take a position that is 100 times the amount of initial margin. If the trader is not careful in setting up the stop-loss, it could quickly deplete your trading account. We’ll see leverage in action with an example shortly.
For example, let;s say a trader has a capital of $1000 in his trading account. He deciced to place a buy order on EUR/USD at 1.1100 for 1 Standard lot by using 1:100 leverage offered by his broker.
If the EUR/USD price goes down by just 100 pips, which is less than 1%, then the trader would lose entire trading capital of $1000. But if the trader is right in his trade, then he can gain from the trade.
But as you can understand from this example, the risks of using excessive leverage to trade forex is very risky. You must never use more than 1:10 leverage.
Another concept related to leverage is margin, which we will explain below.
3. Margin: Margin is the amount needed in your trading account to place an forex trade. Forex brokers set margin requirements to open a trade, and this is the money set aside with the broker when your position is open.
Let's say that you are placing an order for $10,000, with a leverage of 1:100. This would mean that you can place $10,000 order with $100 capital. Your broker would now set that $100 aside as 'margin' from your trading account. If margin goes down below a threshold required by the broker, you will receive a notice from the broker to fill it up to the required levels.
4. Stop Loss: Stop loss is the level that you can set, at your desired price where you decide to exit a losing trade. Losses are inevitable, but how you manage that loss is important. So always remember to set a stop loss whenever you are placing a trade.
Some brokers also offer GSLO (Guaranteed Stop Loss), which guarantees that your position will be closed at the price limit set in your order.
It is really important to have a defined stop loss for risk management. For example, an easy way would be to set stop loss at 2% of you equity per trade. Let's understand it using a real trade example.
If your account equity (basically your balance if you don't have any active positions) is let's say R100,000, the 2% of that would be R2000. You can set the stop loss such that you don't lose more than R2000 on that trade. But it is important to adjust your position sizing accordingly to set your stop loss such that it is an important level where you want to set the actual stop, but also, it must ensure that you don't lose more than 2% on the given trade.
If your account size it smaller (less than $5000), then it is natural to risk more per trade. But still, you must avoid risking more than 10% on a single position, and set your stop loss accordingly.
Now let’s take a real-world example of a trade to better understand all these terms & the dynamics of an actual trade.
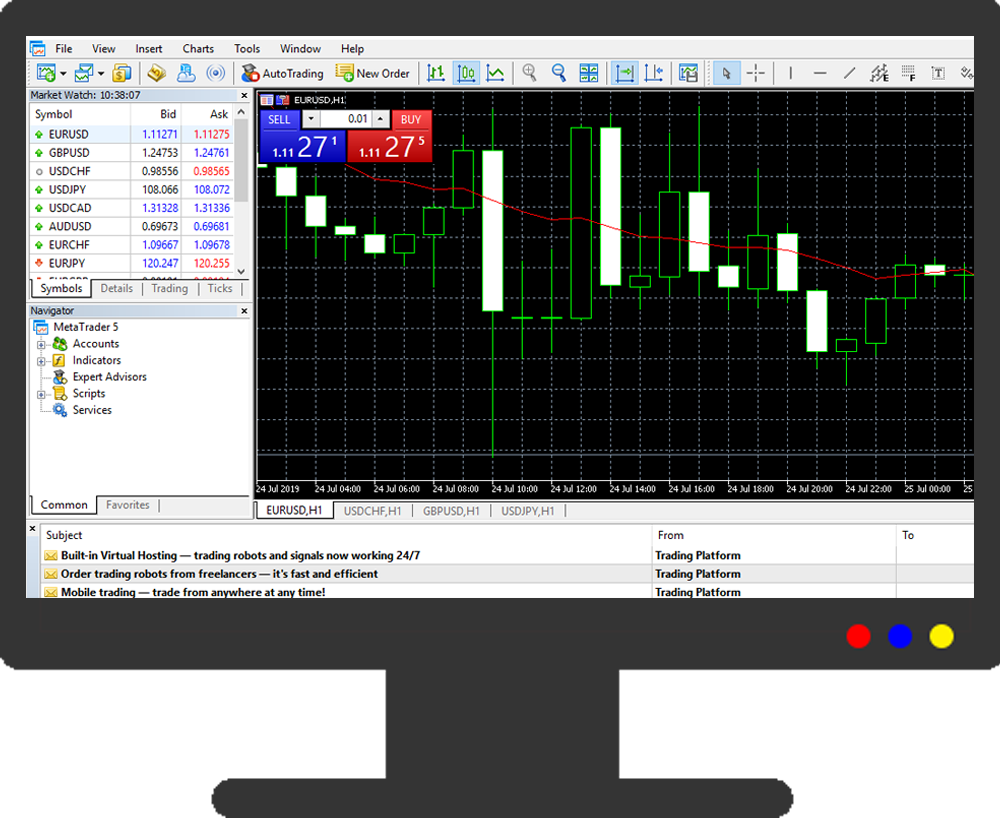
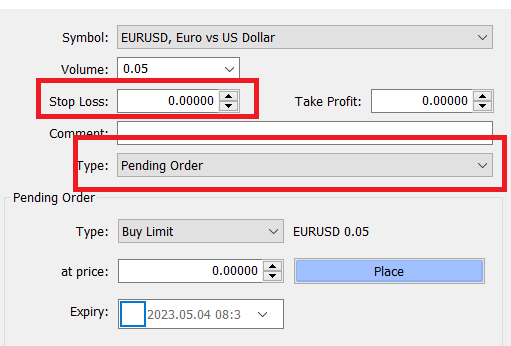
5. Order Types: There are different order types which you can use to place your order in the market through your broker. The most common types are 'Market Order', 'Limit Order' & 'Stop Loss Order'.
With the market order, you are instructing your forex broker to get you the fill immediately. Your buy or sell order will be executed at the nearest bid or ask price available. When you place a buy or a sell order directly (not pending) from your MetaTrader, it is a market order.
With a Limit order, you are instructing your forex broker to get you the fill at a particular price, which could be higher or lower than the currenct exchange rates.
For example, if the EURUSD is trading at 1.1059 Bid, you can place a limit order, to sell EUR/USD at 1.1100, which is higher than the current market price. Your broker will try to fill your order at that price when the exchange rate goes there.
Stop loss order basically helps to limit your loss on a particular trade. For example, let's say you have placed a Buy order on EUR/USD at 1.1045, and you feel that the right place for your Stop loss would be 45 pips lower at 1.1000. You can use Stop Loss order via your MetaTrader to instruct your broker to close your active position once the Ask price goes at or below 1.1000
Below screenshot from MetaTrader 4 of the various order types which you can place during placing a trade.
3) How to place a trade in forex market? – Real world example:
We will now take example of actual trading positions, and how you can place the trade in Forex market.
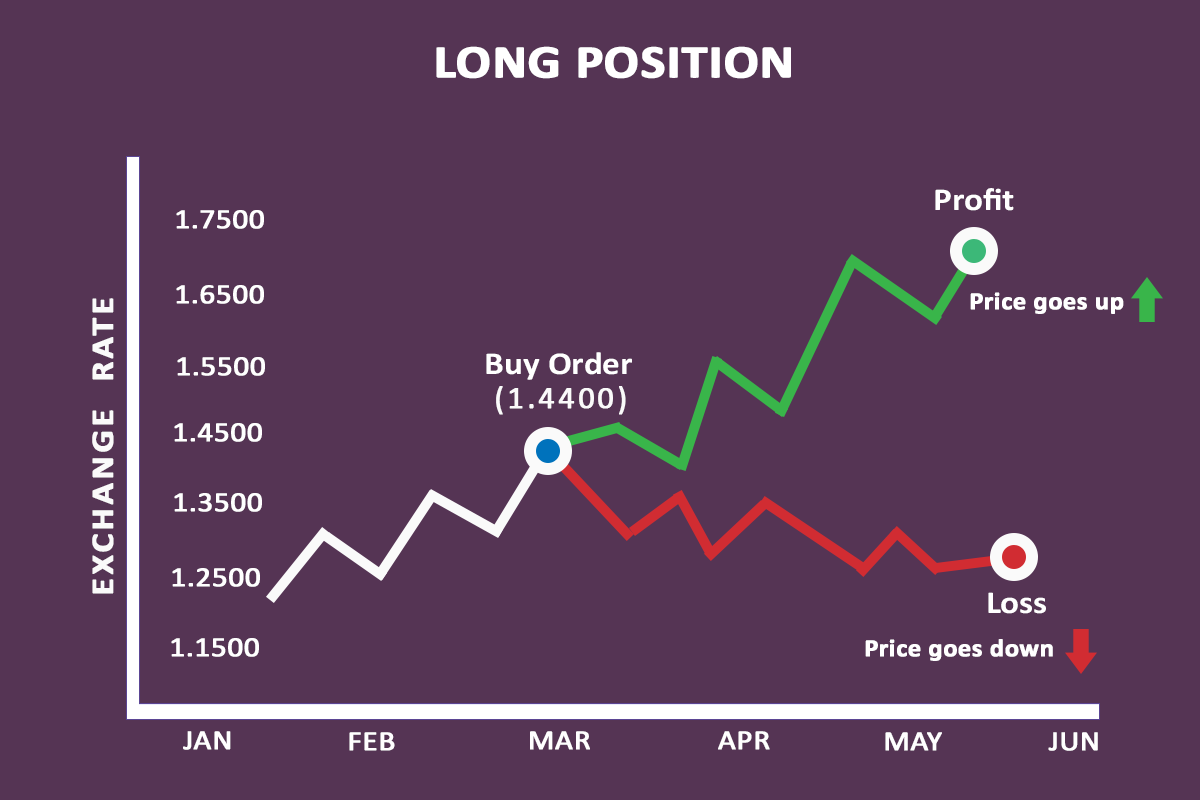
Suppose you have a trading capital of $10,000, and you decide to trade EUR/USD. Let's say the EUR/USD is quoted as 1.4400. You think the EUR is likely to go up against the US Dollar in the next 3 months, so you decided to place a buy order on EUR/USD.
Case 1 – Buy order 1:10 leverage: You want to buy 1 Mini Lot of EUR/USD thinking the EUR might rise in value against the USD. So you’re buying the EUR/USD currency pair, which means you are buying EUR and selling the USD simultaneously. If you buy 1 mini lot, you need to use 10:1 leverage (10*1000 =10,000 units of USD).
Profit case: Let's say that over time, EUR/USD moved up from 1.4400 to 1.7000 i.e. 2600 Pips. Assuming the value of 1 Pip is $1 for 1 mini lot, you stand to gain $2600.
Loss Case: But if the market goes against you, let's say to 1.2600, then the market would have gone 1800 pips against you, so you would have lost $1800.
Below is the example of a Long/Buy Order in Forex.
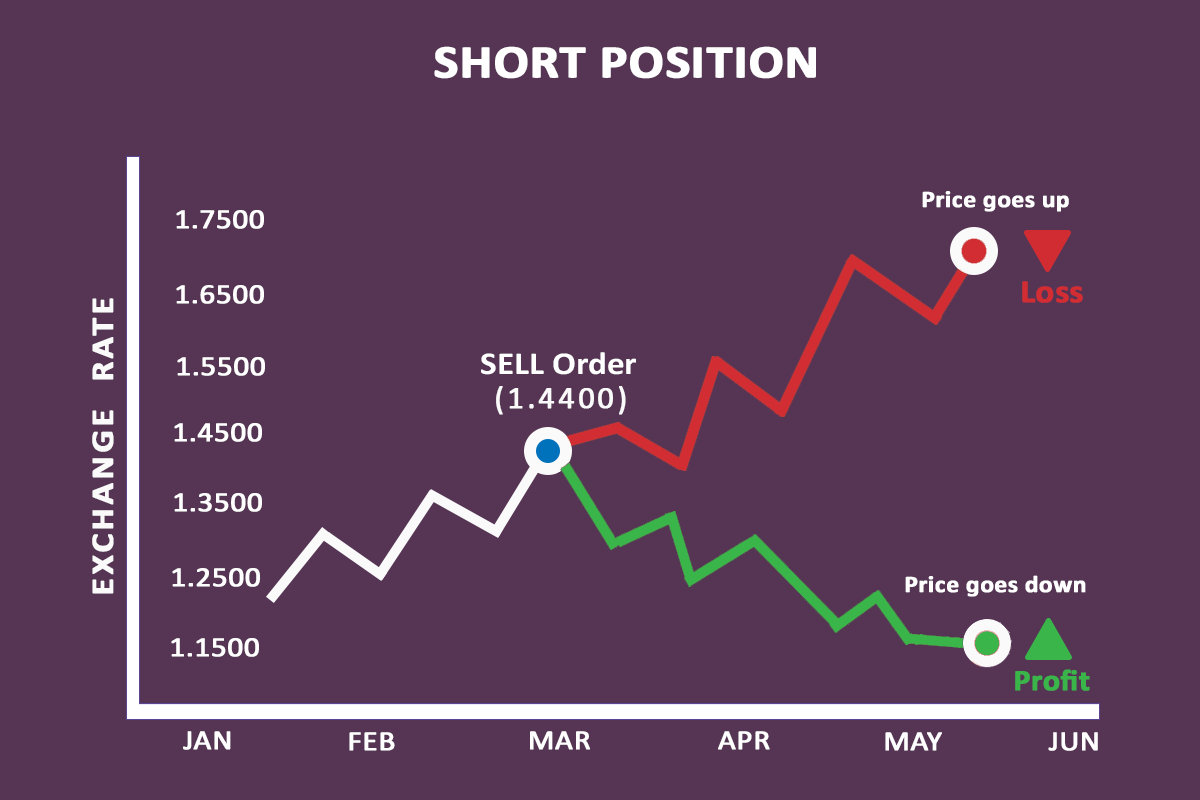
Case 2 – Sell Order with 1:10 leverage: Now, let suppose that you think that EUR has peaked against the USD, and so you decided to sell the EUR/USD. Assume that you have a trading capital of $10,000, and the current price of EUR/USD is 1.4400. You decide to place a sell order on EUR/USD.
Profit case: Let's assume that EUR/USD goes down from 1.4400 to 1.1500 over period of 3 months, about 2900 Pips. If you had placed sell order for 1 Mini lot, then you would stand to gain $2900 for the trade.
Loss Case: In case the market goes up, from 1.4400 to 1.7000, then you would have lost 2600 pips, that is almost $2600 in case of 1 mini lot.
Below is an example of how a Sell Order works in Forex trading.
Both the above cases highlight how you can lose or gain from a forex trade, depending on your position, position size (lots), leverage etc. It is best to fully understand all these dynamics on demo, and then only trade live when you have a proper strategy in place. And always remember to use a Stop-loss for every trade.
Before entering any trade, have a pre-defined risk based off of your strategy. For example, if you are a counter-trend trader, then you should have very small stop-loss.
Let's say, that you have defined the criteria for your entry, and you are willing to risk 40 pips on your trade. One, the Reward on the trade must be higher than 1:2 (80 pips or higher) to consider that order. Two, your position sizing (number of lots you place on that order), must be adjusted such that you are not risking more than 1% of your account balance of one trade.
If you are risking too much of your account on an overleverage position, there is a high chance that you will lose very quickly. Forex Trading is about identifying your edge & managing your risk.
On any given trade there is a chance that it could be a win or a loss. So, if you are risking too much of your capital on any single trade, and you lose that trade, then the equity drawdown would be higher, and you will need to make more to get back to breakeven point.
Let us understand this with a simple example. Let us say you have R10,000 in your account balance, and you risk R1500 on a GBP/USD intraday trade with a 30 pips stop loss. The trade goes against you, and you decide to double down, and increase your risk even more. So, instead of losing 15% of your equity, you would in this example lose even more if the trade goes against you.
No loss is big enough if you are able to take it. That is why you must define your edge & only trade that edge.
If your edge is just trading 'Engulfing' pattern on the weekly (Bullish & Bearish Engulfings) on major currency pairs, then you must only trade that. Assume that you can have a series of losses, few in a row, and take risk accordingly only. 30 trades series is a good rule to have. Follow the exact same strategy for 30 trades in a row, regardless of the outcome of the trade.
So, if you are trading an Engulfing pattern on weekly on all majors, you must take the trade every time it shows up. And you must not risk more than 3.3% of your equity on any single trade. So, if the strategy requires you to place the stop loss few pips above the high of Bearish Engulfing or below of low of Bullish Engulfing, then you must adjust your position sizing accoording.
The exact trade that you enter, may or may not work. But you must execute it regardless.
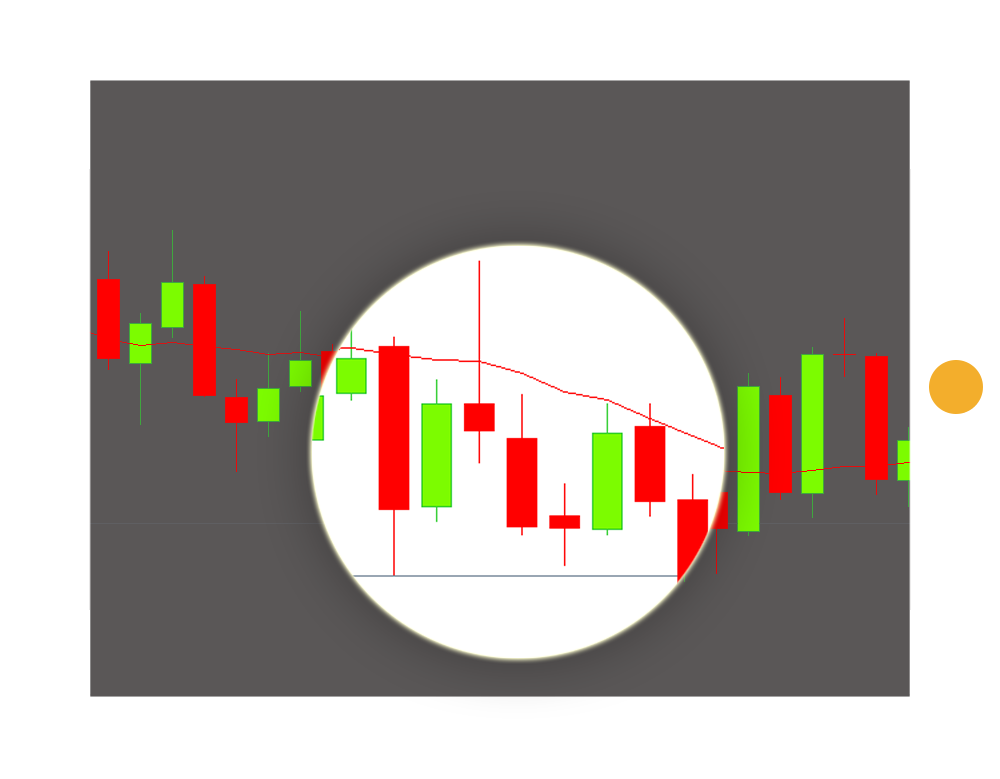
Take the below USD/CAD weekly chart for example. I've marked the Bullish & Bearish Engulfing patterns in space. If you notice, then in then one example you would have been stopped out. In other 3 trades, you would either have a profit or Breakeven if you let the trade run.
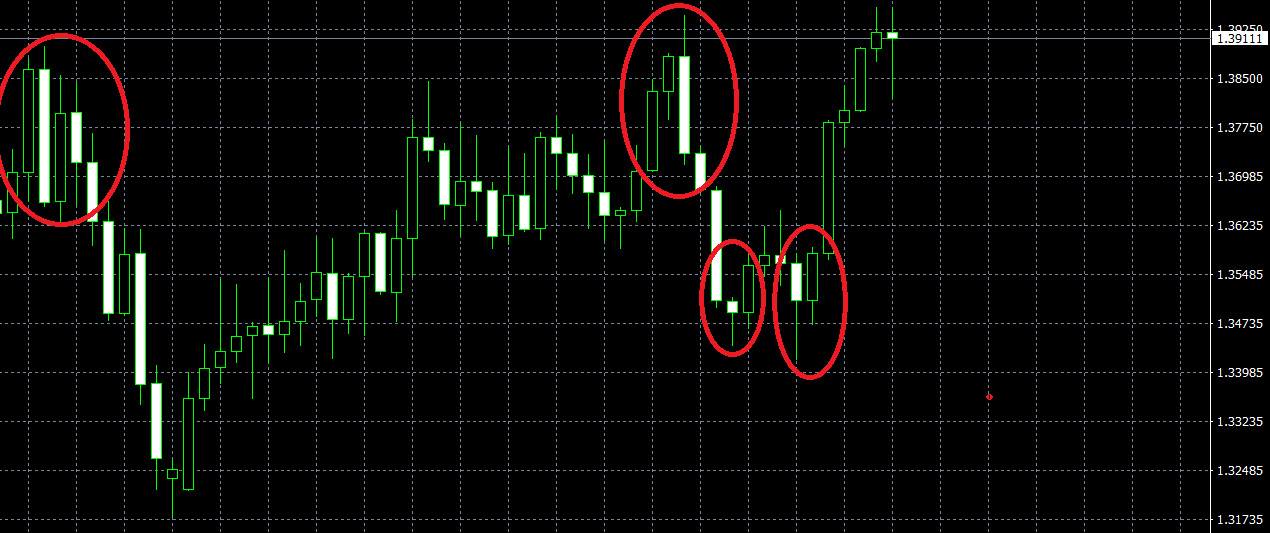
The point here is, when you are executing your edge, you don't know if or not, the trade that you are taking will have a positive outcome. You must change your thinking to series of trades.
On any single trade, you might lose. Also, you could lose 5-6 together (depending on your strategy & market conditions, your next few trades could be losing trades). But you must consider the long-term. If you are able to execute flawlessly, will the strategy be profitable over a series of trades that you will place in a year?
If you can answer this positively, then you have an edge.